Overview
In traditional web applications, data encryption is usually only applied at the transport layer (TLS/HTTPS), and at rest on database server disks:
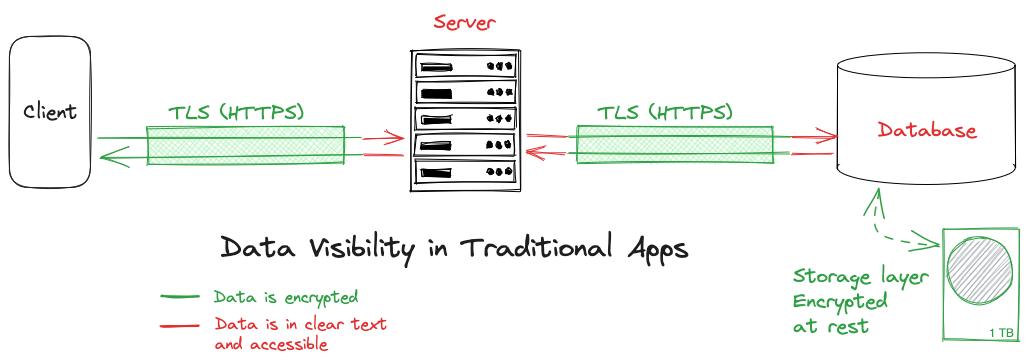
End-to-end encrypted applications have the same guarantees, but add a layer of client-side cryptography that ensures that nobody else than clients has access to clear-text data:
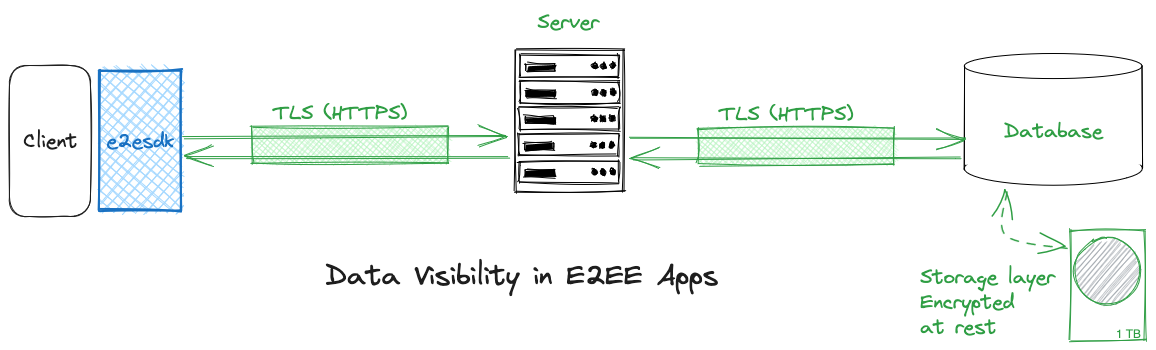
e2esdk is made of two parts:
- Client NPM packages to be installed and used in your front-end application code
- A server that manages identities and encryption keys
Users register their cryptographic identities on the server, and use it to store encrypted keys.
Users can then retrieve those keys to encrypt and decrypt application data.
Users can also choose to securely share keys with others, to access shared workspaces.
The SDK also provides secure ways to ingest structured data from the outside (eg: forms), using public key cryptography.
Data visibility management
For an ideal end-to-end encryption experience, data should be encrypted just before being sent to the server, and decrypted just after being received by the client.
e2esdk is designed to stay out of your way when dealing with application code and domain data, and performs best as a boundary between the client and the server.
Integration with application code
e2esdk makes no assumption on what your application data looks like, how it's stored, or how it's retrieved by the client.
Identities on e2esdk are managed separately from their application equivalent
(eg: a Users table in a database), and only require a unique and immutable
user ID to reference users.
The e2esdk server can talk to your application server via webhook routes, to authorise certain operations it may lack context about, and notify the application server of certain events that may trigger domain-related actions.
Forms
e2esdk has a first-class integration to ingest encrypted data from forms filled by anonymous users.
Anonymity here means that whoever submits an encrypted form does not require a cryptographic identity on e2esdk.
This is particularly useful for public forms.
Form data is encrypted using a combination of symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, only allowing owners of the form private key to decrypt submissions, but also while allowing respondants to edit their own submission.
Files
Both forms and regular encryption operations allow encrypting files.
File contents are encrypted using individual symmetric keys, stored in the file metadata, along with the filename, clear text size and modification date.
This metadata object can then be encrypted like any other data before being submitted to the application server.
This lets clients decrypt the lightweight metadata object first, allowing the UI to display useful information, and giving users the choice of downloading and decrypting file contents on demand.
Key types
There are two kinds of keys in e2esdk:
sealedBoxasymmetric key pairs (public + private keys)secretBoxsymmetric keys
sealedBox key pairs are used for anonymous/public form submissions.
You would send the public key to the respondant, which they'd use to encrypt
form data into a submission. On the other side, form owners would use the
associated private key to decrypt the submssion.
secretBox keys are used for symmetric access to information: whoever has
access to it can both read (decrypt) and write (encrypt). Those keys are ideal
for workspaces where users may wish to invite someone later on: sharing the
workspace keys with a newcomer gives them access to all the encrypted content,
and allows them to encrypt new content as well.
A third key type, box, is reserved for a future update of the SDK to allow
direct data exchange between two users. This system is already in use to share
keys, but may be extended in the future to implement secure messaging
(using modern cryptographic guarantees like forward secrecy).
Key sharing
Unless your application only allows users accessing their own data, you'll need to share keys with other users, to share access to the underlying data they operate on.
Key sharing is a first party mechanism in e2esdk. It allows users to:
- share keys securely with others
- list participants who have access to a particular set of keys
- manage their pending invitations
- ban users who no longer need access to a key and rotate it
- manage permissions for sets of keys
Security
Secret key material is never exposed outside of the e2esdk client for security purposes. The application interacts with the e2esdk client through fingerprints, non-secret references to an underlying secret.
All sensitive data (key material) is end-to-end encrypted by the e2esdk client before being sent to the e2esdk server. The default server configuration requires TLS certificates for an end-to-end HTTPS transport between the client and server.
The client and server use mutual authentication in their API exchanges, to rule out a man-in-the-middle meddling with request/response payloads.